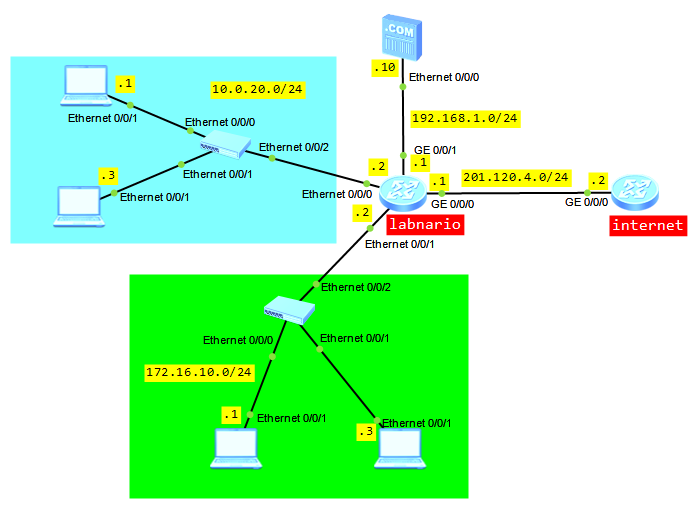
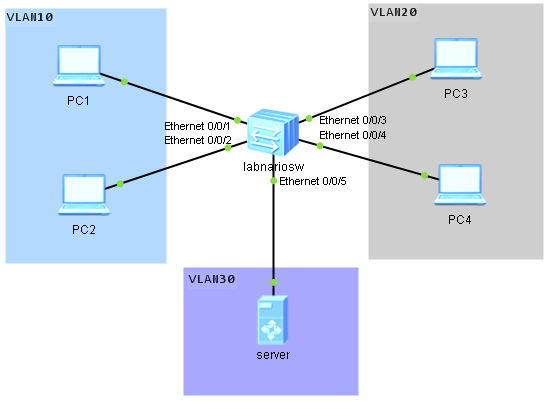
When a single switch is upgraded, services are interrupted about 3 minutes. This time increases when a stack is upgraded. Methods of upgrading the system software of S5300 and S6300 are the same. We can focus on Huawei S5300 switch as an example. Let’s assume we have 2 switches in the stack.
<labnario> display stack
Stack topology type: Ring
Stack system MAC: 80fb-06b1-69eb
MAC switch delay time: 10 min
Stack reserved vlanid : 100
Slot# role Mac address Priority Device type
------ ---- -------------- ------ -------
0 Master 80fb-06b1-69eb 100 S5352C-EI
1 Standby 80fb-06ab-f6e3 120 S5352C-EI
At first you have to check a space of flash memory of the switch. If there is no enough space in the flash to fit a new system software, just delete the old (current) system software, for both Master and Member switches:
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch