OSPF stub area on Huawei router
Instead of transmitting learned AS external routes, area border router, in a stub area, generates a default route and advertises the route to non-ABRs in the stub area. In short, stub area reduces entries in the routing table of ABR and the amount of routing information to be transmitted.
We have to remember that:
- The backbone area cannot be a stub area
- All routers in a stub area need to be configured using stub attributes
- The ASBR cannot exist in a stub area
- Virtual links cannot be configured in stub area.
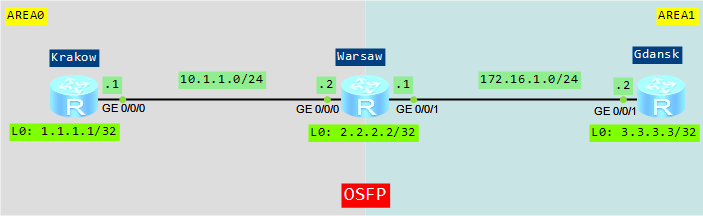
Let’s try to configure a simple lab. We would like to see what happens if AREA1 becomes a stub area.
- Based on the topology, configure IP address of each interface.
- Enable OSPF on each router and configure basic OSPF functions
- Configure AREA1 as stub and and check routing information on router Gdansk.
- Check routing information on router Gdansk, previously stopping advertising type 3 LSA into the stub area.
PIM SM on Huawei S5700
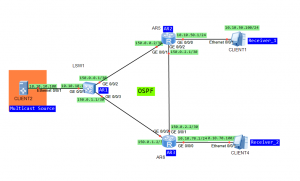
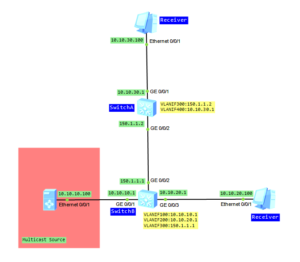
I wanted to use AR routers to prepare PIM SM lab but it turned out that there is a problem with cooperation between multicast source and AR router. Of course I am talking about network simulator eNSP. Finally I decided to use eNSP with S5700. So we have topology like in the last two posts:
- Configure VLANs, VLAN interfaces and IP addresses based on the topology (omitted).
- Configure OSPF to ensure connectivity between switches (omitted).
- Enable multicast on both switches.
- Enable PIM SM on all interfaces.
- Enable IGMP on receivers’ interfaces.
- Set static RP for both switches (Loopback0 of SwitchB).
- Address of multicast group G: 225.1.1.1.
- Address of multicast group S: 10.10.10.100.
HCIE-R&S Info Session (not available any more)
Useful information for those who think or want to pass Huawei certification. A session about HCIE certification process and exam contents by Nigel Roy.

PIM DM control messages
To understand how PIM DM works, just look at control messages generated.
Let’s take topology from the last lab:
After PIM DM is configured on interfaces between neighbors, both devices periodically send HELLO messages to each other, to discover neighbors and maintain the neighbor relationship:
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch