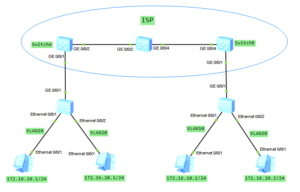
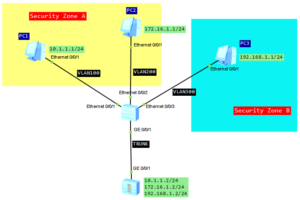
Let’s go ahead with QinQ technology. In the last post you had the opportunity to know basic QinQ tunneling on Huawei switches. The QinQ tunnel attaches the same outer tag to all the frames entering the Layer 2 QinQ interface.
In this lab I would like to attach different outer tags, to the frames entering the Layer 2 QinQ interface, according to different inner tags. It is useful when packets are going to be differentiated in a provider’s network. Why? Because of service type, user’s application etc.
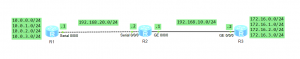
In this case we have 1 enterprise network with branch office located in another city. Customer network is divided into 2 VLANs to differentiate existing services. Our task is to transparently transmit packets, through ISP network, paying attantion to not allowing traffic between VLAN10 and VLAN20.
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch