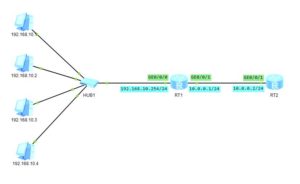
You, as the network administrator, were tasked with providing access to a network, where 4 machines have been connected.
It is simple task. Nothing can happen, but…
Everything is ready and you are checking connectivity between RT2 and those machines, and… To your suprise, you can only ping even-numbered IP addresses:
[RT2]ping 192.168.10.1
PING 192.168.10.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Request time out
Request time out
Request time out
Request time out
Request time out
[RT2]ping 192.168.10.2
PING 192.168.10.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 192.168.10.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=127 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.10.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=127 time=20 ms
Reply from 192.168.10.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=127 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.10.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=127 time=40 ms
Reply from 192.168.10.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=127 time=30 ms
[RT2]ping 192.168.10.3
PING 192.168.10.3: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Request time out
Request time out
Request time out
Request time out
Request time out
[RT2]ping 192.168.10.4
PING 192.168.10.4: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 192.168.10.4: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=127 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.10.4: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=127 time=40 ms
Reply from 192.168.10.4: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=127 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.10.4: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=127 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.10.4: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=127 time=30 ms
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch