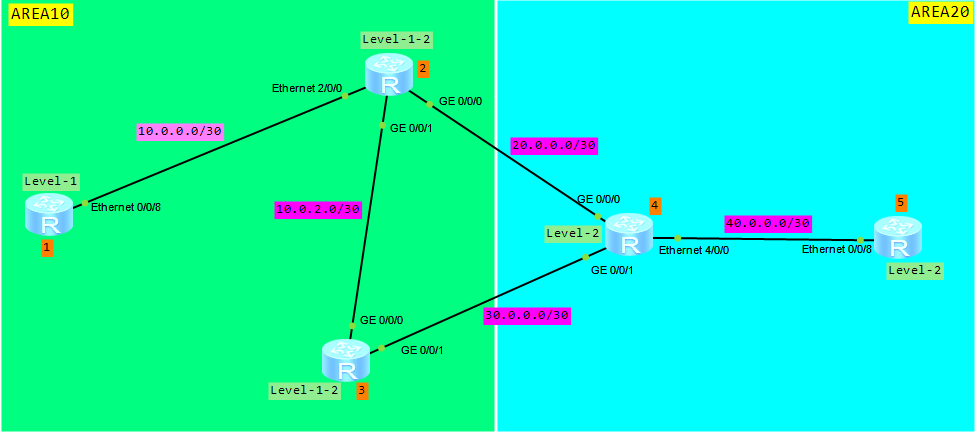
Let’s keep going and try to configure ISIS route aggregation based on the following topology:
If you want to recall how to configure ISIS adjacency on Huawei routers, just go to ‘ISIS on Huawei routers‘.
To avoid DIS election, configure all physical interfaces as ISIS point-to-point (p2p) links (Router 1 as an example):
[1-Ethernet0/0/8]isis circuit-type p2p
[1]dis isis interface
Interface information for ISIS(1)
---------------------------------
Interface Id IPV4.State IPV6.State MTU Type DIS
Eth0/0/8 003 Up Down 1497 L1/L2 --
Loop0 001 Up Down 1500 L1/L2 --
Loop100 002 Up Down 1500 L1/L2 --
[1]dis isis interface Ethernet 0/0/8 verbose
Interface information for ISIS(1)
---------------------------------
Interface Id IPV4.State IPV6.State MTU Type DIS
Eth0/0/8 003 Up Down 1497 L1/L2 --
Circuit MT State : Standard
Circuit Parameters : p2p
Description : HUAWEI, AR Series, Ethernet0/0/8 Interface
SNPA Address : 00e0-fc03-993e
IP Address : 10.0.1.1
IPV6 Link Local Address :
IPV6 Global Address(es) :
Csnp Timer Value : L12 10
Hello Timer Value : 10
DIS Hello Timer Value :
Hello Multiplier Value : 3
Cost : L1 10 L2 10
Ipv6 Cost : L1 10 L2 10
Retransmit Timer Value : L12 5
LSP-Throttle Timer : L12 50
Bandwidth-Value : Low 100000000 High 0
Static Bfd : NO
Dynamic Bfd : NO
Fast-Sense Rpr : NO
Extended-Circuit-Id Value : 0000000003
What we want to do today are:
- Configure Loopback100 interface on Router 1 and assign 10.0.100./32 IP address to it
- Enable ISIS protocol on Loopback100
- Configure three static routes: 10.0.2.0/24, 10.0.3.0/24, 10.0.4.0/24 on Router 1
- Import the static routes to ISIS
- Aggregate these networks on Level-1-2 router (router 2).
Let’s do it. Configure Loopback100 and enable ISIS on it:
[1]interface LoopBack 100 [1-LoopBack100]ip address 10.0.100.1 32 [1-LoopBack100]isis enable
Configure static routes on Router 1 to simulate networks that should be aggregated:
[1]ip route-static 10.0.2.0 255.255.255.0 NULL0 [1]ip route-static 10.0.3.0 255.255.255.0 NULL0 [1]ip route-static 10.0.4.0 255.255.255.0 NULL0
Import these three routes into ISIS:
[1]isis [1-isis-1]import-route static level-1
Check the routing table of Router 1:
[1]dis ip rout
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Routing Tables: Public
Destinations : 16 Routes : 16
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/0 ISIS-L1 15 10 D 10.0.1.2 Ethernet0/0/8
1.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack0
2.2.2.2/32 ISIS-L1 15 10 D 10.0.1.2 Ethernet0/0/8
10.0.1.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 10.0.1.1 Ethernet0/0/8
10.0.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
10.0.1.3/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
10.0.2.0/24 Static 60 0 D 0.0.0.0 NULL0
10.0.3.0/24 Static 60 0 D 0.0.0.0 NULL0
10.0.4.0/24 Static 60 0 D 0.0.0.0 NULL0
10.0.100.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack100
20.0.0.0/30 ISIS-L1 15 20 D 10.0.1.2 Ethernet0/0/8
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Check the routing table of Router 5 to find how our networks have been advertised:
[5]dis ip routing-table
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Routing Tables: Public
Destinations : 17 Routes : 17
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
1.1.1.1/32 ISIS-L2 15 30 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
2.2.2.2/32 ISIS-L2 15 20 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
4.4.4.4/32 ISIS-L2 15 10 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
5.5.5.5/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack0
10.0.1.0/30 ISIS-L2 15 30 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
10.0.2.0/24 ISIS-L2 15 94 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
10.0.3.0/24 ISIS-L2 15 94 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
10.0.4.0/24 ISIS-L2 15 94 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
10.0.100.1/32 ISIS-L2 15 30 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
20.0.0.0/30 ISIS-L2 15 20 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
40.0.0.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 40.0.0.2 Ethernet0/0/8
40.0.0.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
40.0.0.3/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
These three static routes configured on Router 1 are imported into ISIS and we can find them in the routing table of Router 5. It should be noted that ISIS has no external routes, unlike OSPF. The origin of the routes is still ISIS, with preference 15. As you can see, the IP address of Loopback100 of Router 1 is also found in the routing table of Router 5.
Let’s finally configure route aggregation. Based on the topology and networks configured, we can aggregate the following networks on Router 2:
- 10.0.1.0/30
- 10.0.2.0/24
- 10.0.3.0/24
- 10.0.4.0/24
- 10.0.100.1/32.
[2]isis [2-isis-1]summary 10.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 (Level-2 by default)
Verify the IP routing table of Router 5 once again:
[5]dis ip routing-table
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Routing Tables: Public
Destinations : 13 Routes : 13
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
1.1.1.1/32 ISIS-L2 15 30 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
2.2.2.2/32 ISIS-L2 15 20 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
4.4.4.4/32 ISIS-L2 15 10 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
5.5.5.5/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack0
10.0.0.0/16 ISIS-L2 15 30 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
20.0.0.0/30 ISIS-L2 15 20 D 40.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
40.0.0.0/30 Direct 0 0 D 40.0.0.2 Ethernet0/0/8
40.0.0.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
40.0.0.3/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Ethernet0/0/8
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Thus the routing table has been reduced.
Read More » Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch