To understand how PIM DM works, just look at control messages generated.
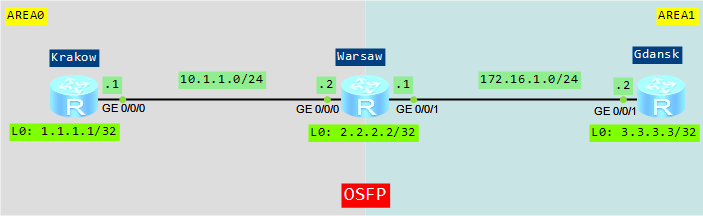
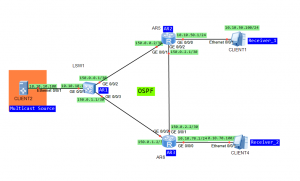
Let’s take topology from the last lab:
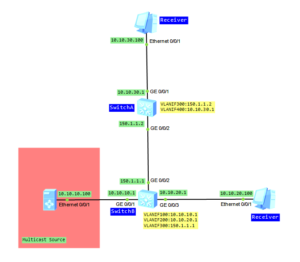
After PIM DM is configured on interfaces between neighbors, both devices periodically send HELLO messages to each other, to discover neighbors and maintain the neighbor relationship:
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.2-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): PIM ver 2 HEL se
nding 150.1.1.2 -> 224.0.0.13 on Vlanif300 (P012213)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.3-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): Option: 1, lengt
h: 2 (P012260)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.4-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): Holdtime: 105 (P
012278)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.5-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): Option: 19, leng
th: 4 (P012260)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.6-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): DR priority: 1 (
P012324)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.7-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): Option: 20, leng
th: 4 (P012260)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.8-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): GenID: 0X9FBFC09
E (P012343)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.9-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): Option: 2, lengt
h: 4 (P012260)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.10-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): Tbit: unset (P
012300)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.11-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): Lan delay: 500
(P012303)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.12-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): Override interv
al: 2500 (P012306)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.13-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): Option: 21, len
gth: 4 (P012260)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.14-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): Version: 1 (P01
2365)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.15-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): Refresh interva
l: 60 (P012368)
Jul 4 2014 13:16:44.940.16-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/NBR:(public net): Reserved: 00000
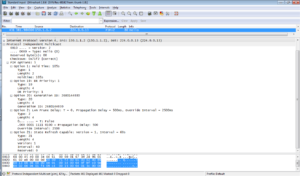
A PIM device must first receive HELLO message from its neighbor before it can receive multicast packets, to create multicast routing entries and maintain the MDT.
Once the PIM neighbor relationship is established, multicast source floods multicast data to all routers on the network. PIM DM assumes that at least one multicast group member exists on each subnet. That’s why all routers receive multicast data. Then PIM DM prunes brunches that don’t have multicast receivers and forward traffic only to brunches that require to receive multicast data. In such case JOIN/PRUNE message is sent by PIM router that doesn’t need multicast traffic.
Jul 4 2014 12:57:44.250.1-08:00 SwitchB PIM/7/JP:(public net): PIM ver 2 JP rec
eiving 150.1.1.2 -> 224.0.0.13 on Vlanif300 (P012998)
Jul 4 2014 12:57:44.250.2-08:00 SwitchB PIM/7/JP:(public net): Upstream 150.1.1.
1, Groups 1, Holdtime 210 (P013002)
Jul 4 2014 12:57:44.250.3-08:00 SwitchB PIM/7/JP:(public net): Group: 225.1.1.1/
32 --- 0 join 1 prune (P013011)
Jul 4 2014 12:57:44.250.4-08:00 SwitchB PIM/7/JP:(public net): Prune: 10.10.10.1
00/32 (P013021)
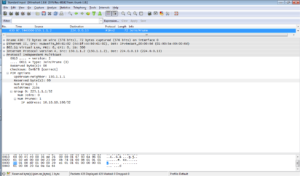
At the same time network brunches send JOIN/PRUNE messages to receive multicast data. Format of this message is the same like PRUNE message.
Jul 7 2014 12:24:19.300.3-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/JP:(public net): PIM ver 2 JP sen
ding 150.1.1.2 -> 224.0.0.13 on Vlanif300 (P012933)
Jul 7 2014 12:24:19.300.4-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/JP:(public net): Upstream 150.1.1.
1, Groups 1, Holdtime 0 (P012939)
Jul 7 2014 12:24:19.300.5-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/JP:(public net): Group: 225.1.1.1/
32 --- 1 join 0 prune (P012949)
Jul 7 2014 12:24:19.300.6-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/JP:(public net): Join: 10.10.10.10
0/32 (P012959)
In PIM DM network, to avoid that the interface restores forwarding because the prune timer times out, the first hop router, nearest to the source, periodically triggers STATE-REFRESH messages:
Jul 7 2014 12:39:31.530.1-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/SRM:(public net): PIM ver 2 SRM re
ceiving 150.1.1.1 -> 224.0.0.13 on Vlanif300 (D191471)
Jul 7 2014 12:39:31.530.2-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/SRM:(public net): Group address: 2
25.1.1.1/32 flags: 00000000 (D191476)
Jul 7 2014 12:39:31.530.3-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/SRM:(public net): Source address:
10.10.10.100 (D191481)
Jul 7 2014 12:39:31.530.4-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/SRM:(public net): Originator addre
ss: 150.1.1.1 (D191485)
Jul 7 2014 12:39:31.530.5-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/SRM:(public net): preference: 0 me
tric: 0 mask length: 24 (D191514)
Jul 7 2014 12:39:31.530.6-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/SRM:(public net): ttl: 255 prune i
ndicator: set prune now: unset assert override: set (D191518)
Jul 7 2014 12:39:31.530.7-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/SRM:(public net): interval: 60 (D1
91524)
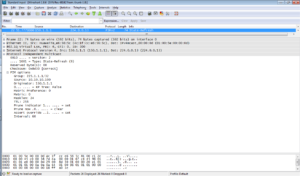
Once a receiver wants to join multicast group, it sends IGMP report to upstream device:
Jul 7 2014 13:32:45.290.1-08:00 SwitchA IGMP/7/EVENT:(S,G) creation event receiv
ed for (10.10.10.100/32, 225.1.1.1/32). (G01985)
Jul 7 2014 13:32:45.290.2-08:00 SwitchA IGMP/7/EVENT:No state in global MRT. Not
merging downstream for (10.10.10.100/32, 225.1.1.1/32) on interface Vlanif300(15
0.1.1.2). (G011016)
Jul 7 2014 13:32:50.650.1-08:00 SwitchA IGMP/7/REPORT:Received v2 report for gro
up 225.1.1.1 on interface Vlanif400(10.10.30.1) (G082859)
Jul 7 2014 13:32:50.650.2-08:00 SwitchA IGMP/7/EVENT:Creating group(225.1.1.1) f
or interface Vlanif400(10.10.30.1) (G014427)
Jul 7 2014 13:32:50.650.3-08:00 SwitchA IGMP/7/TIMER:Enqueue group(225.1.1.1) on
interface Vlanif400(10.10.30.1) in group_calq. (G016648)
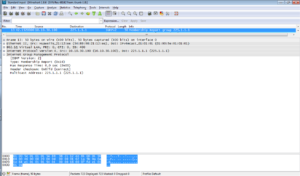
After PIM router receives the report message from the host, it sends a GRAFT message through the upstream interface of the related (S, G) entry, if the router is not on the SPT (shortest path tree). Upstream device responds with GRAFT-ACK message and restores the forwarding status of the downstream interface connected to requesting device.
Jul 4 2014 12:55:53.950.1-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/JP:(public net): PIM ver 2 GFT sen
ding 150.1.1.2 -> 150.1.1.1 on Vlanif300 (P012933)
Jul 4 2014 12:55:53.950.2-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/JP:(public net): Upstream 150.1.1.
1, Groups 1, Holdtime 0 (P012939)
Jul 4 2014 12:55:53.950.3-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/JP:(public net): Group: 225.1.1.1/
32 --- 1 join 0 prune (P012949)
Jul 4 2014 12:55:53.950.4-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/JP:(public net): Join: 10.10.10.10
0/32 (P012959)
Jul 4 2014 12:55:53.960.1-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/JP:(public net): PIM ver 2 GAK rec
eiving 150.1.1.1 -> 150.1.1.2 on Vlanif300 (P012933)
Jul 4 2014 12:55:53.960.2-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/JP:(public net): Upstream 150.1.1.
2, Groups 1, Holdtime 0 (P012939)
Jul 4 2014 12:55:53.960.3-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/JP:(public net): Group: 225.1.1.1/
32 --- 1 join 0 prune (P012949)
Jul 4 2014 12:55:53.960.4-08:00 SwitchA PIM/7/JP:(public net): Join: 10.10.10.10
0/32 (P012959)
PIM-DM employs GRAFT to implement fast data forwarding and enable new group members to rapidly receive multicast data.
In case of our receiver is connected to both PIM routers in our topology, in the shared network segment, the PIM device receives (S, G) packet from the downstream interface of the (S, G) or (*, G) entry. It means that other forwarders exist in the network segment. That’s why PIM device sends an ASSERT message through the downstream interface to take part in the election. The router that fails the election, stops forwarding multicast data through the downstream interface:
Jul 4 2014 15:59:43.910.2-08:00 SwitchB PIM/7/ASSERT:(public net): Fsm:assert, c
urrent state: winner received event: 10 for (10.10.10.100,225.1.1.1) on interface
Vlanif400 (D02701)
Using debugging command and Wireshark on eNSP you can simply check how PIM DM works. You can find messages’ types, default parameters and so on. I chose only control messages, generated by PIM routers, here in this post.
Read More »
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch