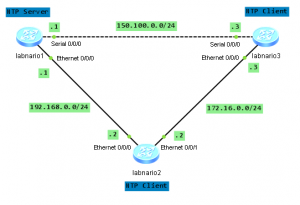
Let’s take Huawei’s S3328TP-SI switch as an example. This switch has 2 combo ports, which can be changed either to optical or electrical mode.
[Quidway]display elabel ... [Board Properties] BoardType=CX5Z228AM BarCode=21023513816TA9000116 Item=02351381 Description=Quidway S3328TP-SI,CX5Z228AM,S3328TP-SI Mainframe(24 10/100 BASE-T ports and 2 Combo GE(10/100/1000 BASE-T+100/1000 Base-X) ports and 2 SFP GE (1000 BASE-X) ports (SFP Req.) and AC 110/220V) Manufactured=2010-09-28 VendorName=Huawei IssueNumber= CLEICode= BOM= ...

Use ‘display interface …” command to check port mode of the interface:
[Quidway]display interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/4
GigabitEthernet0/0/4 current state : UP
Line protocol current state : UP
Description:HUAWEI, Quidway Series, GigabitEthernet0/0/4 Interface
Switch Port,PVID : 1,The Maximum Frame Length is 1600
IP Sending Frames' Format is PKTFMT_ETHNT_2, Hardware address is 286e-d49b-8c17
Port Mode: COMBO AUTO
Current Work Mode: FIBER
Speed : 1000, Loopback: PHY
Duplex: FULL, Negotiation: DISABLE
Last 300 seconds input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Last 300 seconds output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Input peak rate 0 bits/sec,Record time: -
Output peak rate 0 bits/sec,Record time: -
Input: 0 packets, 0 bytes
Unicast : 0,Multicast : 0
Broadcast : 0,Jumbo : 0
CRC : 0,Giants : 0
Jabbers : 0,Throttles : 0
Runts : 0,DropEvents : 0
Alignments : 0,Symbols : 0
Ignoreds : 0,Frames : 0
Discard : 0,Total Error : 0
Output: 0 packets, 0 bytes
Unicast : 0,Multicast : 0
Broadcast : 0,Jumbo : 0
Collisions : 0,Deferreds : 0
Late Collisions: 0,ExcessiveCollisions: 0
Buffers Purged : 0
Discard : 0,Total Error : 0
Input bandwidth utilization threshold : 100.00%
Output bandwidth utilization threshold: 100.00%
Input bandwidth utilization : 0.00%
Output bandwidth utilization : 0.00%
You have 3 options in combo-port command:
- auto – selects the interface type automatically
- copper – uses the electrical interface
- fiber – uses the optical interface.
As you can see in the above output, port mode is COMBO AUTO, SFP module has been inserted and current work mode is automatically chosen as FIBER.
To display optical power of SFP module:
[Quidway]display transceiver interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/4 verbose GigabitEthernet0/0/4 transceiver information: ------------------------------------------------------------- Common information: Transceiver Type :OC48_SHORT_REACH_SFP Connector Type :LC Wavelength(nm) :1310 Transfer Distance(m) :5000(90um) Digital Diagnostic Monitoring :YES Vendor Name :FINISAR CORP. Ordering Name : ------------------------------------------------------------- Manufacture information: Manu. Serial Number :'P6R282H Manufacturing Date :2004-12-18 Vendor Name :FINISAR CORP. ------------------------------------------------------------- Diagnostic information: Temperature(ĄăC) :44.00 Temp High Threshold(ĄăC) :93.00 Temp Low Threshold(ĄăC) :-30.00 Voltage(V) :3.30 Volt High Threshold(V) :3.70 Volt Low Threshold(V) :2.90 Bias Current(mA) :25.76 Bias High Threshold(mA) :70.00 Bias Low Threshold(mA) :4.00 RX Power(dBM) :-33.69 RX Power High Threshold(dBM) :-1.00 RX Power Low Threshold(dBM) :-20.00 TX Power(dBM) :-6.14 TX Power High Threshold(dBM) :-1.02 TX Power Low Threshold(dBM) :-11.52 -------------------------------------------------------------
Verbose option displays detailed information about the optical module, including the basic information, manufacturing information, alarm information and diagnosis information.
Read More » Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch