A short NAT (Network Address Translation) description based on AR1200 documentation:
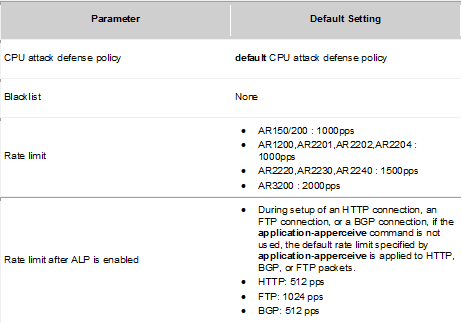
Huawei AR1200 supports the following NAT features: static NAT, port address translation (PAT), internal server, NAT Application Level Gateway (ALG), NAT filtering, NAT mapping, Easy IP, twice NAT, and NAT multi-instance.
The number of private addresses is equal to the number of public addresses, so it does not save pull of public addresses.
Maps a public address to multiple private addresses.
Hosts in the public network can access an internal server.
Takes a public IP address of the interface as the source address after NAT is performed.
Translates both the source and destination addresses. Using in the scenario where IP addresses of hosts on private and public networks overlap.
Allows users on private networks to access the public network and allows users in different VPNs to access the public network through the same egress. In addition, users in the VPNs with the same IP address can access the public network. Supports association between VPNs and NAT server, and allows users on the public network to access hosts in the VPNs. This function is applicable when IP addresses of multiple VPNs overlap.
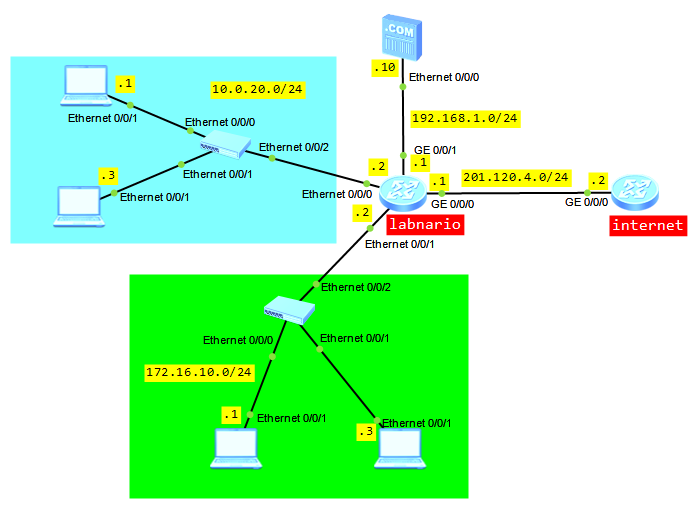
Let’s try to configure NAT based on the below topology:
- Users from LAN 10.0.20.0/24 can access internet using a pull of public addresses.
- Users from LAN 172.16.10.0/24 can access internet using a public IP of WAN interface.
- Users from internet can access internal FTP server 192.168.1.10.
Configure IP addresses and default routing based on the above topology:
labnario
#
interface Vlanif100
ip address 10.0.20.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlanif200
ip address 172.16.10.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ethernet0/0/0
portswitch
port link-type access
port default vlan 100
#
interface Ethernet0/0/1
portswitch
port link-type access
port default vlan 200
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 201.120.4.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 201.120.4.2
internet
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 201.120.4.2 255.255.255.0
Configure outbound NAT on labnario router for hosts in both LANs:
[labnario]acl number 2000
[labnario-acl-basic-2000] rule 5 permit source 10.0.20.0 0.0.0.255
[labnario]acl number 2500
[labnario-acl-basic-2500] rule 5 permit source 172.16.10.0 0.0.0.255
[labnario]nat address-group 1 201.120.4.100 201.120.4.110
[labnario]interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0
[labnario-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]nat outbound 2000 address-group 1 no-pat
[labnario-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]nat outbound 2500
[labnario-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]display this
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 201.120.4.1 255.255.255.0
nat outbound 2000 address-group 1 no-pat
nat outbound 2500
No-pat indicates one-to-one NAT, that is, only the IP address is translated and the port number is not translated.
Configure NAT server on labnario router to let external users to have FTP access to internal FTP server:
[labnario-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]nat server protocol tcp global 201.120.4.10 ftp inside 192.16.1.10 ftp
Enable the NAT ALG function for FTP packets:
[labnario]nat alg ftp enable
[labnario]display nat alg
NAT Application Level Gateway Information:
----------------------------------
Application Status
----------------------------------
dns Disabled
ftp Enabled
rtsp Disabled
sip Disabled
----------------------------------
After the NAT ALG function is enabled for an application protocol, packets of the application protocol can traverse the NAT server. The application protocol cannot work without the NAT ALG function.
Let’s check if our NAT is configured properly:
[labnario]display nat outbound
NAT Outbound Information:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Interface Acl Address-group/IP/Interface Type
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 2000 1 no-pat
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 2500 201.120.4.1 easyip
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total : 2
[labnario]dis nat server
Nat Server Information:
Interface : GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Global IP/Port : 201.120.4.10/21(ftp)
Inside IP/Port : 192.16.1.10/21(ftp)
Protocol : 6(tcp)
VPN instance-name : ----
Acl number : ----
Description : ----
Total : 1
Unfortunately, even NAT commands are supported by eNSP simulator, it does not mean that NAT is supported as a whole. Internal hosts cannot communicate with internet and internal FTP server is not available for public users as well. But this is what I wanted to show you. You can check this NAT configuration on real devices. It should work properly.
Read More »
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch