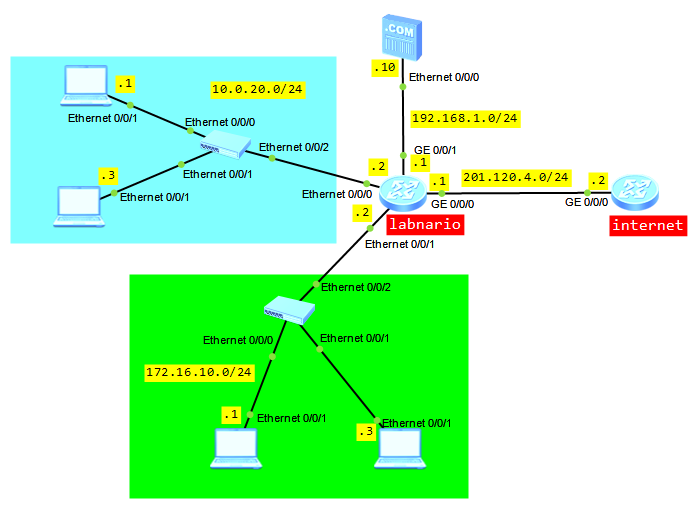
We have waited for a new version of Huawei eNSP simulator since February 1st, 2013.
And we have finally got it.
Quite new and fresh V100R002C00B110 version.
New look … new devices … new connections …
We have waited for a new version of Huawei eNSP simulator since February 1st, 2013.
And we have finally got it.
Quite new and fresh V100R002C00B110 version.
New look … new devices … new connections …
Today a few words about 2 simple but useful commands: lock and send.
LOCK – prevents unauthorized users from operating on the current terminal interface
SEND – enables the system to transfer messages between user interfaces
Let’s look how they work on Huawei S5700 switch.
<labnario>lock Enter Password: Confirm Password: Info: The terminal is locked. Enter Password: <labnario>
When a single switch is upgraded, services are interrupted about 3 minutes. This time increases when a stack is upgraded. Methods of upgrading the system software of S5300 and S6300 are the same. We can focus on Huawei S5300 switch as an example. Let’s assume we have 2 switches in the stack.
<labnario> display stack
Stack topology type: Ring
Stack system MAC: 80fb-06b1-69eb
MAC switch delay time: 10 min
Stack reserved vlanid : 100
Slot# role Mac address Priority Device type
------ ---- -------------- ------ -------
0 Master 80fb-06b1-69eb 100 S5352C-EI
1 Standby 80fb-06ab-f6e3 120 S5352C-EI
At first you have to check a space of flash memory of the switch. If there is no enough space in the flash to fit a new system software, just delete the old (current) system software, for both Master and Member switches:
A short NAT (Network Address Translation) description based on AR1200 documentation:
Huawei AR1200 supports the following NAT features: static NAT, port address translation (PAT), internal server, NAT Application Level Gateway (ALG), NAT filtering, NAT mapping, Easy IP, twice NAT, and NAT multi-instance.
Let’s assume that a large number of packets are sent to CPU of a device. What will happen if most of these packets are malicious attack packets? CPU usage will become high, what can bring to services’ deterioration. In extreme cases it can lead the device to reboot. We can minimize an impact of the attack on network services, providing the local attack defense function. When such attack occurs, this function ensures non-stop service transmission.