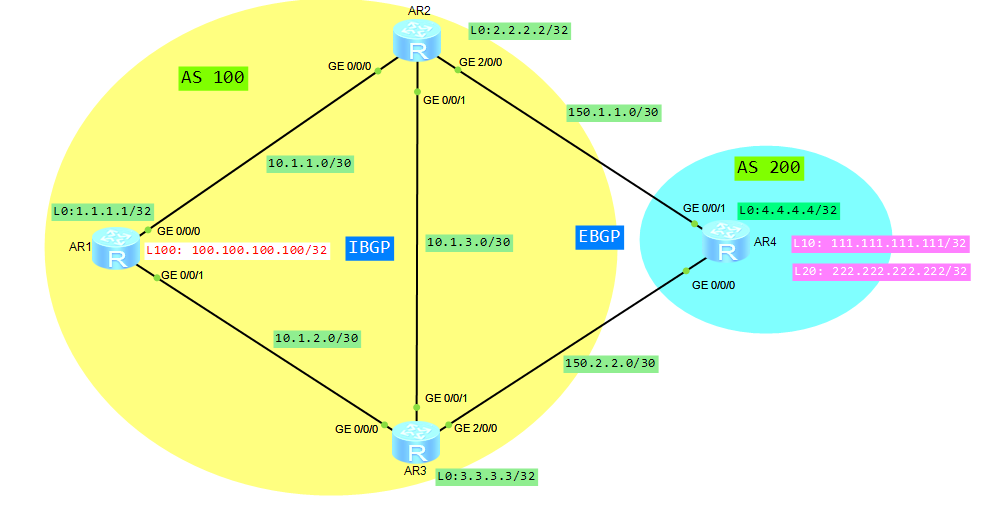
I have come across link flapping protection feature recently. It is available on S5700 switches. It looks like it is a new feature on Huawei switches. I had not met it in older hardware versions. That’s why I decided to write a few words about it. Unfortunatelly, although this command is available in Huawei network simulator eNSP, it does not work properly. But maybe you will have possibility check it on your real devices.
Port flapping (port going UP and DOWN continually) can be caused by a faulty cable, link failure, active/standby switchover, port hardware failure, etc. Frequent status changes on an interface can lead to:
- STP topology recalculation and changes,
- ARP entries updates,
- dynamic routing instability and convergence problems.
All these issues can negatively affect switch performance and should be avoided.
Link Flapping Protection is a feature that can be implemented on an interface to solve problems caused by the flapping port or link. It checks the interface flapping frequency and link flapping detection interval. If the number of interface flapping times reaches the limit, in a specified period, the interface is shut down.
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch