When PCs are in a different subnet than a DHCP server installed, DHCP Relay Agent can be used to forward DHCP requests from PCs to DHCP server. How to configure DHCP Relay Agent using Huawei CLI?
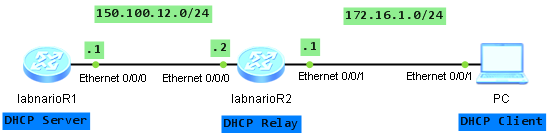
Let’s assume that we have the following topology:
We want our PC to acquire its IP address from the DHCP server configured on the labnarioR1 router. To do so, labnarioR2 should be configured as a DHCP Relay Agent to forward DHCP Requests and Offers between server and clients.
First, DHCP server should be configured. LabnarioR1 router will be configured to offer DHCP service for PC.
<labnarioR1>system-view Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z. [labnarioR1] dhcp enable [labnarioR1] ip pool 1 [labnarioR1-ip-pool-1] gateway-list 172.16.1.1 [labnarioR1-ip-pool-1] network 172.16.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 [labnarioR1-ip-pool-1] dns-list 150.100.15.1 150.100.15.2 [labnarioR1-ip-pool-1] domain-name labnario.com [labnarioR1-ip-pool-1] quit [labnarioR1]interface Ethernet0/0/0 [labnarioR1-Ethernet0/0/0]dhcp select global
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch