There are two interface backup modes:
- Active/standby
- Load balancing
In common active/standby mode only one interface transmit services at any time. When active interface works properly, it transmit all the traffic. In case of fault of the primary interface, a backup interface with the highest priority starts transmitting packets. If primary interface recovers, traffic is switched back to active interface.
In load balancing mode, in case traffic volume exceeds an upper threshold set for active interface, a backup interface with the highest priority starts transmitting packets and load balancing is performed.
Which mode we have is determined by upper and lower thresholds. If thresholds are not set, active/standby mode is used. Otherwise, load balancing mode is used.
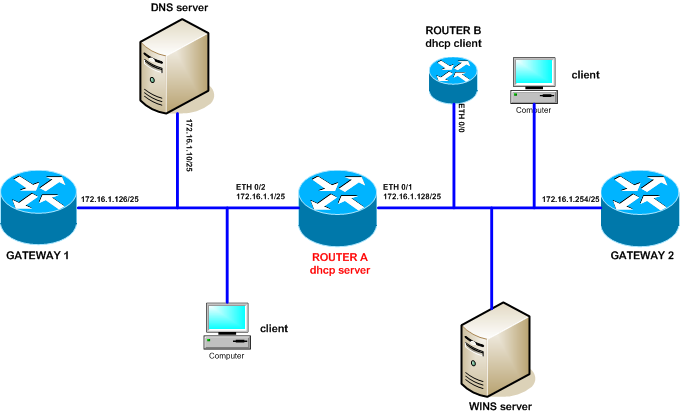
Let’s assume that we have the following topology:
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch