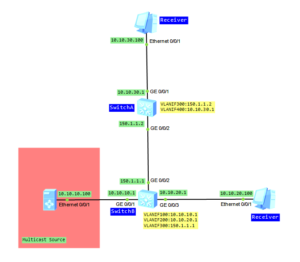
- Configure IP addresses based on the above topology (omitted).
- Use OSPF to assure connectivity between switches.
- Enable multicast on both switches.
- Enable PIM DM on all interfaces.
- Address of multicast group G: 225.1.1.1.
- Address of multicast group S: 10.10.10.100.
OSPF configuration:
[SwitchA]dis current-configuration configuration ospf # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.10.30.0 0.0.0.255 network 150.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 # [SwitchB]display current-configuration configuration ospf # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.10.20.0 0.0.0.255 network 150.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 #
Although PIM is intra-domain multicast routing protocol, RPF check is always performed based on IGP, in our case OSPF. Every problem in OSPF causes a problem in the multicast.
Enable multicast on both switches:
[SwitchA]multicast routing-enable [SwitchB]multicast routing-enable
Enable PIM DM on each interface:
[SwitchA]dis cur int Vlanif # interface Vlanif300 ip address 150.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 pim dm # interface Vlanif400 ip address 10.10.30.1 255.255.255.0 pim dm igmp enable [SwitchB]dis cur int Vlanif # interface Vlanif100 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 pim dm igmp enable # interface Vlanif200 ip address 10.10.20.1 255.255.255.0 pim dm igmp enable # interface Vlanif300 ip address 150.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 pim dm #
As you can see from the above output, except PIM DM protocol, IGMP has been configured at the interfaces towards receivers. What is IGMP? This is Internet Group Management Protocol that manages IPv4 multicast members. In short, IGMP needs to be enabled on hosts and on switches. Through IGMP, a multicast L3 device knows whether there is a multicast group member, on the network segment to which an interface of the switch is connected.
Verification (SwitchA as an example):
[SwitchA]display pim interface VPN-Instance: public net Interface State NbrCnt HelloInt DR-Pri DR-Address Vlanif300 up 1 30 1 150.1.1.2 (local) Vlanif400 up 0 30 1 10.10.30.1 (local) [SwitchA]dis pim neighbor VPN-Instance: public net Total Number of Neighbors = 1 Neighbor Interface Uptime Expires Dr-Priority BFD-Session 150.1.1.1 Vlanif300 00:57:23 00:01:22 1 N [SwitchA]dis igmp interface Interface information Vlanif400(10.10.30.1): IGMP is enabled Current IGMP version is 2 IGMP state: up IGMP group policy: none IGMP limit: - Value of query interval for IGMP (negotiated): - Value of query interval for IGMP (configured): 60 s Value of other querier timeout for IGMP: 0 s Value of maximum query response time for IGMP: 10 s Querier for IGMP: 10.10.30.1 (this router)
Let’s start multicast source. Assume that receivers need to get information about multicast group G 225.1.1.1. When sending multicast packets to multicast group G, multicast source S 10.10.10.100 generates an SPT (shortest-path tree) through flooding and the (S, G) entries exist on both switches that are in the SPT. When a receiver joins multicast group G, an (*, G) entry is generated on the switch.
[SwitchA]dis pim routing-table
VPN-Instance: public net
Total 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(*, 225.1.1.1)
Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: WC
UpTime: 00:00:07
Upstream interface: NULL
Upstream neighbor: NULL
RPF prime neighbor: NULL
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlanif400
Protocol: igmp, UpTime: 00:00:07, Expires: never
(10.10.10.100, 225.1.1.1)
Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: ACT
UpTime: 00:12:17
Upstream interface: Vlanif300
Upstream neighbor: 150.1.1.1
RPF prime neighbor: 150.1.1.1
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlanif400
Protocol: pim-dm, UpTime: 00:00:07, Expires: -
[SwitchB]dis pim routing-table
VPN-Instance: public net
Total 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry
(*, 225.1.1.1)
Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: WC
UpTime: 00:00:30
Upstream interface: NULL
Upstream neighbor: NULL
RPF prime neighbor: NULL
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 1
1: Vlanif200
Protocol: igmp, UpTime: 00:00:30, Expires: never
(10.10.10.100, 225.1.1.1)
Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: LOC ACT
UpTime: 00:12:37
Upstream interface: Vlanif100
Upstream neighbor: NULL
RPF prime neighbor: NULL
Downstream interface(s) information:
Total number of downstreams: 2
1: Vlanif300
Protocol: pim-dm, UpTime: 00:00:25, Expires: never
2: Vlanif200
Protocol: pim-dm, UpTime: 00:00:30, Expires: -
Let’s check whether it works, using eNSP with VLC.
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch