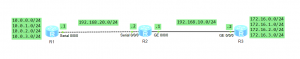
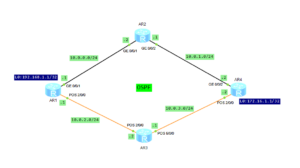
I am going to show you how RIP loop protection works. Let’s take the topology from the previous post to demonstrate the features.
There are 2 methods of loop protection: Split Horizon and Poison Reverse.
Split Horizon
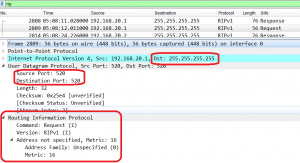
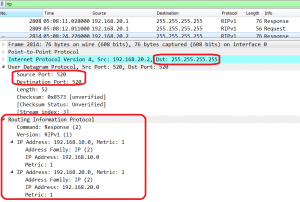
It prohibits a router to advertise a route back to neighbors, through the interface that receives the routes. Split Horizon is enabled by default on Huawei routers:
[R1]display rip 1 interface Serial 0/0/0 verbose Serial0/0/0(192.168.20.1) State : UP MTU : 500 Metricin : 0 Metricout : 1 Input : Enabled Output : Enabled Protocol : RIPv2 Multicast Send version : RIPv2 Multicast Packets Receive version : RIPv2 Multicast and Broadcast Packets Poison-reverse : Disabled Authentication type : None Replay Protection : Disabled
Split Horizon is disabled
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch