As you probably know there are five types of OSFP packets:
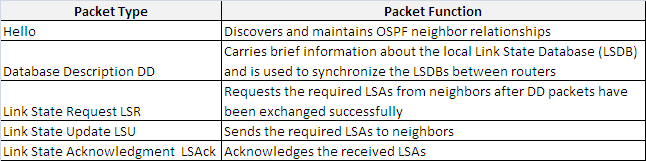
All these packets, except Hellos, are sent only between adjacent routers.
LSA types
There are 5 common LSA types:
- Router-LSA and Network-LSA calculate intra-area routes describing detailed link state information.
- Network-Summary-LSA calculates inter-area routes describing brief routing information instead of link state information
- ASBR-Summary-LSA describes how to reach ASBR
- AS-External-LSA describes how to reach destinations outside AS.
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch
