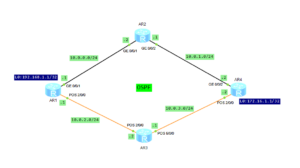
What do we have in traditional IP networks?
Let’s assume that there is a fault at the physical or data link layers. Router sees that a physical interface becomes DOWN. After the router detects this fault, it informs upper layer routing system to update routing information. The convergence time is several seconds, what is critical for sensitive services.
That’s why IP FRR has been developed. After we configure IP FRR, a router doesn’t wait for network convergence but a backup link is immediately used to forward packets.
We have 2 scenarios of using IP FRR:
- To protect routers in public networks.
- To protect CE routers in private networks.
Let’s focus on the first one.
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch

