I’ve had only one case when I used this command and … full success.
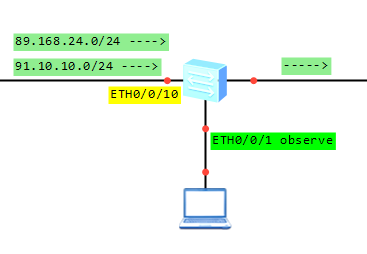
Sometimes it can happen that the file system doesn’t work properly. When you run dir command, you can find the space, which usage status is unknown. The system prompts you that the file system should be restored. Then you can run fixdisk command to release the unknown space.
Notice that:
- It is not recommended to use it when the file system works correctly.
- It doesn’t help when physical medium is damaged.
- Do not use it when CPU usage is high.
Lost chains in flash detected, please use fixdisk to recover them! <labnario>fixdisk flash: Fixdisk flash: will take long time if needed %Fixdisk flash: completed.
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch