Topology Change (TC) packets are sent when MSTP-enabled interface in a network flaps. If a physical interface frequently alternates between Up and Down, the MSTP status of the device in the network becomes unsteady. As a result, a large number of TC messages are generated, ARP entries are frequently deleted and services are interrupted.
How to find the source of TC packets?
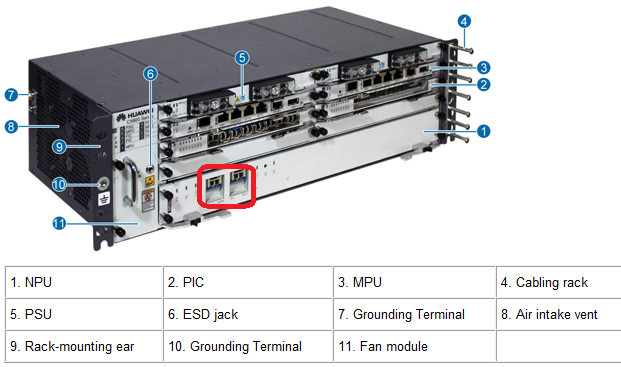
Let’s look at the log, generated on one of the switches in a network. Let’s take Huawei S9300 switch as an example:
Dec 19 2012 11:32:56+10:00 S9300 %%01MSTP/6/RECEIVE_MSTITC(l)[40922]:MSTP received BPDU with TC, MSTP process 0 instance 0, port name is GigabitEthernet6/0/0.
What can we find in this log?
The most important for us is the port number on which the switch received TC packet, in this case interface GE6/0/0. To troubleshoot this problem we have to go to the next switch, connected to interface GE6/0/0 and check logs of that switch. If the neighbouring switch receives TC packets as well, we have to do further troubleshooting. If we find in the logs that MSTP-enabled interface is flapping, we can consider that this interface is the source of the TC packet. If this interface is still flapping, just make it down, to avoid unsteady behaviour.
 Labnario Huawei From Scratch
Labnario Huawei From Scratch